View crop
View crop Data sheet EcoPortIpomoea batatas
 |
|
| Notes |
|---|
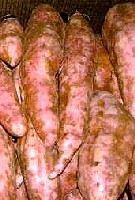
| DESCRIPTION: An herbaceous vine with a creeping growth habit. The plant forms tuberous roots that are mostly located within the top 25 cm of the soil. Tubers vary largely in shape, colour and texture. The stems form running vines up to 4 m long, usually prostrate and slender, with milky juice, lateral stem-branches arising from the short stem are not usually branched. The leaves are variable, ovate-cordate, borne singly on long petioles, palmately veined, angular or lobed, depending on variety, green or purplish. At the end of the vine, trumpet shaped hermaphrodite flowers are formed during the summer; they are white or pale violet, axillary, funnel-shaped, borne singly or in cymes on short peduncles. They are, however, rare, especially in United States. In late summer and spring the plant forms round pods with flattened, hard-coated, angular seeds and there are 1-4 seed per pod. USES: It is cultivated for its edible tubers. They are eaten boiled, baked, candied with syrup, or pureed and they are processed like potatoes into fried chips, starch, flour, glucose and they can be canned and dehydrated. The tubers have a high concentration of carbohydrates in the form of sugar and starch. Plant tops and leaves are used as potherbs and the vine as a fodder. Greatly esteemed as feed for farm animals; with 3 kg green sweet potatoes equivalent to 1 kg of maize, with a food value rated 95-100% that of maize. Dry vines a have feed value which compares favorably with alfalfa hay as forage The sweet potato is being regarded as a valuable raw material for producing alcohol bio-fuel. The leaf decoction is used medicinally. KILLING T.: May be damaged below 10°C. Very sensitive to temperatures below 1°C for brief periods and 3°C for longer periods. GROWING PERIOD: Warm-season perennial herb, cultivated as an annual, may be harvested after 80-360 days. A frost-free period of 110-170 days is necessary. COMMON NAMES: Sweet potato, Spanish potato, Louisiana yam, Patate douce, Artichaut des Indes, Bataat, Zoete aardappel, Shaharkuand, Camote, Batata, Batate susskartoffel, Skurar-kanda, Mita-alu, Ketala, Rambet, Ubi jalar, Kamote, Uara, Kumara, Satsuma-imo, Kara-imo, Imo, Doukali, Dankali, Anamo, Veeazee, Viazi viamu, Apichu, Getica, Papas, Mabi. FURTHER INF.: Grown between latitudes 40°N and 32°S at elevations up to 2800 m in equatorial regions, and otherwise up to about 2000 m. The species is indigenous to Central America, and the north-western part of South America. Distinct differences between day and night temperatures encourage the formation of tuberous roots. A photoperiod of less than 11 hours induces flowering, less flowering occurs at 12 hours and none at all at 13 hours daylight. Above 30°N and S little flowering occurs. Low humidity as the crop approaches maturity is beneficial. Vine cuttings are usually used for planting or transplants produced by bedding mother roots or from rooted cuttings. Optimum yields vary from 17.5 to 27.5 t/ha depending on the cultivar and growing conditions, while average yields are 5 t/ha in Africa, 10 t/ha in South America and 16 t/ha in Asia. The world highest production yield at 80 t/ha has been obtained in Israel. It is one of only seven world food crops with an annual production of more than 100 million metric tons. 1 ton of roots remove 4 kg N, 1 kg P and 7 kg K from the field. The photosynsthesis pathway is C 3 II. | Sources |
| Purdue NewCROP Plants For A Future USDA Plants Wikipedia Sims D (pers. comm.) Rice R 1990 pp 285-287 [TEMP, RAIN, LIG, PHO, DRA, TEXT, PH] Maas E 1990 pp 279 [SAL] Sys C 1984 pp 70 Sys C 1990 pp 13 Rhem S 1991 pp 45-48 [TEMP, KTMP, PHO, RAIN, LIG, DRA, PH, SAL] Kassam A 1976 pp 63 Tindall H 1983 pp 100-104 [TEXT, DRA, PH, TEMP, RAIN, LIG, PHO] Landon J 1984 pp 281 291 [TEXT, DRA, PH, FER] Roecklein J 1987 pp 470 [USE] Eswaran H 1986 Kung P 1970 pp 209 Purseglove J 1974 pp 79-88 [TEMP, RAIN, DRA, TEXT, PHO] Nair P 1980 pp 111-115 [RAIN, TEMP, TEXT, FER, DRA, USE] Onwueme I 1991 pp 267-275 [TEMP, LIG, PHO, RAIN, TEXT, DRA, PH] Hartmann T 1981 pp 586-587 [KTMP, TEMP, DRA, TEXT, FER, SAL, RAIN] Hackett C 1985a [PH, LIG, KTMP, TEMP, DEP, SAL, FER] |